Force is one of the most fundamental ideas in physics and a core topic for IB Physics, Analysis Math, and other international curricula. Whether you’re taking IB online courses, learning from IB tutors, or searching for IB tutoring online, understanding force clearly will help you succeed across many topics—especially mechanics.
In this detailed guide from IB Demystified, we’ll explain the unit of force, its definition, formulas, real-life meaning, and its importance for International Baccalaureate (IB) students. This article is written in clear, human language while maintaining academic accuracy—perfect for students aiming to improve their IB score with expert guidance.
The unit of force is a standard measurement used to express how strong a force is. In physics, force describes a push or pull that can change an object’s motion, shape, or direction.
In the International System of Units (SI), the unit of force is called the Newton (N).
✅ 1 Newton (N) is defined as the force required to accelerate a 1 kg mass at a rate of 1 meter per second squared (1 m/s²).
This definition is extremely important for IB Physics, Application Math, and IB mathematics because it directly connects force to motion using equations.
Force is not just a definition you memorize—it’s a concept you apply repeatedly in exams and real-life situations.
Understanding motion (mechanics)
Solving problems in IB Physics
Applying formulas in Analysis Math
Real-world engineering and technology
Scoring well with the help of IB tutors
In fact, mechanics-based questions make up a significant part of IB Physics exams. Students taking IB tutoring online often focus on mastering force early because it simplifies many advanced topics later.
One Newton (N) is the force that:
Acts on a 1 kg object
Causes an acceleration of 1 m/s²
Mathematically:
Force (F)=mass (m)×acceleration (a)
This formula is derived from Newton’s Second Law of Motion, which is a cornerstone concept taught in IB Physics and supported strongly by IB math courses.
Let’s break down the Newton into base SI units:
1N=1kg⋅m/s²
This shows why understanding units is just as important as understanding concepts—something emphasized by expert IB tutors during IB tutoring online sessions.
F=ma
This is one of the most frequently tested formulas in IB Physics and IB examinations.
F=ma
Students taking IB online courses often practice this formula extensively because it links physics directly to IB mathematics tutor concepts.
For every action force, there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
This law explains:
Walking
Rocket propulsion
Collisions
Understanding this clearly is crucial for students aiming for a high IB score.
Although the Newton is the standard unit, other units of force exist:
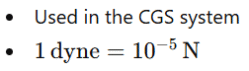
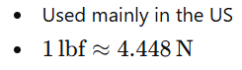
In International Baccalaureate tutoring, focus remains on SI units, especially the Newton.
Attraction between masses
Weight = mass × gravity
Unit: Newton
Opposes motion
Depends on surface and normal force
Force transmitted through ropes or strings
Perpendicular reaction force from a surface
All of these are measured in Newtons, and students practicing with IB tutors online often solve mixed problems involving multiple forces.
Kinematics
Dynamics
Work, energy, and power
Circular motion
Momentum
If you’re enrolled in IB tutoring online with expert IB tutors, force-related problems are usually covered early and revisited often.
Confusing mass with weight
Using incorrect units
Forgetting vector directions
Skipping free-body diagrams
Professional IB tutoring emphasizes concept clarity rather than rote memorization.
Force problems often require:
Algebraic manipulation
Graph interpretation
Vector resolution
Trigonometry
This is why many students combine IB Physics tutoring with an IB mathematics tutor to strengthen overall performance.
Understanding force becomes easier when linked to daily life:
Pushing a door 🚪
Braking a car 🚗
Lifting a bag 🎒
Kicking a ball ⚽
Each action applies force measured in Newtons.
At IBDemystified.com, we support students through:
Personalized IB tutoring online
Structured IB online courses
Concept-based learning in IB physics
Step-by-step guidance by expert IB tutors
Our approach ensures you don’t just learn formulas—you understand them.
The SI unit of force is the Newton (N).
The Newton is derived from Newton’s Laws of Motion, directly linking force to mass and acceleration.
Yes. Weight is the gravitational force acting on an object and is measured in Newtons.
Yes. Weight is the gravitational force acting on an object and is measured in Newtons.
Through consistent practice, conceptual understanding, and guidance from IB tutors or IB tutoring online programs.
Understanding the unit of force is a foundation stone for success in IB Physics, Application Math, and beyond. The Newton (N) is more than a unit—it’s a gateway to understanding motion, energy, and real-world physics.
With the right support from IB Demystified, expert IB tutors, and structured IB online courses, mastering force becomes straightforward and confidence-building.
If your goal is a higher IB score and strong conceptual clarity, start with the basics—and force is the perfect place to begin.

IB Demystified is a trusted online learning platform led by certified IB examiners and educators.
© 2026 IB Demystified LTD
ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Powered by AfiaDigital
WhatsApp us